Understanding the difference between “withdraw” and “withdrawal” is crucial for clear and accurate communication in English. Many learners often ask about the **difference between withdraw and withdrawal**. Simply put, “withdraw” refers to the action of taking something back, whereas “withdrawal” refers to the act or state of that action. To remember which to use, check whether the sentence requires a verb (action) or a noun (thing, process, or state).
For example, “I need to withdraw money” uses the verb, while “The withdrawal of funds took longer than expected” uses the noun. This clarification helps avoid common mistakes and ensures your writing is both precise and grammatically correct.
These two words, derived from the same root, function differently in sentences, with “withdraw” serving as a verb and “withdrawal” acting as a noun.
Using them interchangeably can lead to grammatical errors and confusion. This article provides a comprehensive guide to mastering the correct usage of “withdraw” and “withdrawal,” complete with definitions, examples, and practice exercises.
Whether you’re an English language learner, a student, or simply someone looking to refine their grammar skills, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to confidently use these words in the appropriate context.
This article is designed for anyone who wants to improve their English grammar skills, especially those who find the distinction between verbs and nouns challenging. It is also beneficial for ESL students, writers, and editors who aim to produce polished and error-free content.
Table of Contents
- Definition of Withdraw and Withdrawal
- Structural Breakdown
- Types and Categories
- Examples of Withdraw and Withdrawal
- Usage Rules
- Common Mistakes
- Practice Exercises
- Advanced Topics
- FAQ
- Conclusion
Definition of Withdraw and Withdrawal
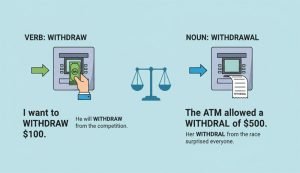
To effectively use “withdraw” and “withdrawal,” it’s essential to understand their definitions and grammatical functions. “Withdraw” is a verb, while “withdrawal” is a noun.
This fundamental difference dictates how they are used in sentences.
Withdraw (Verb)
Definition: To remove, retract, or take back something; to move away or retreat; to cease participation or involvement.
Classification: Verb (action word)
Function: Describes an action of removing, retreating, or ceasing involvement.
Contexts:
- Financial: To take money out of an account.
- Military: To retreat or pull back troops.
- Personal: To remove oneself from a social situation or commitment.
- Statements: To retract or take back a statement.
Withdrawal (Noun)
Definition: The act of withdrawing; the process or state of removing or retreating; the symptoms experienced when stopping the use of an addictive substance.
Classification: Noun (person, place, thing, or idea)
Function: Names the action, process, or state of withdrawing.
Contexts:
- Financial: The act of taking money out of an account.
- Medical: The symptoms experienced when stopping substance use.
- Military: The act of retreating troops.
- General: The act of removing oneself from a situation.
Structural Breakdown
Understanding the structural elements of “withdraw” and “withdrawal” involves examining their verb tenses and noun forms, respectively. This section breaks down how each word is used within a sentence.
Withdraw (Verb)
The verb “withdraw” follows standard verb conjugation rules in English. Here’s a breakdown of its forms:
- Base Form: withdraw
- Past Simple: withdrew
- Past Participle: withdrawn
- Present Participle/Gerund: withdrawing
- Third-Person Singular Present: withdraws
Example sentence using different verb tenses:
- I withdraw money from the bank every week. (Present Simple)
- She withdrew her application yesterday. (Past Simple)
- He has withdrawn all his savings. (Present Perfect)
- They are withdrawing their troops from the border. (Present Continuous)
- The company withdraws its support for the project. (Third-Person Singular Present)
Withdrawal (Noun)
As a noun, “withdrawal” can be singular or plural. Its plural form is “withdrawals.” It can be used as a subject, object, or complement in a sentence.
Example sentences using “withdrawal” as a noun:
- The withdrawal of funds was unexpected. (Subject)
- He made a withdrawal from his account. (Object)
- Her sudden silence was a sign of withdrawal. (Complement)
- The bank recorded multiple withdrawals today. (Plural)
Types and Categories
Both “withdraw” and “withdrawal” can be categorized based on the context in which they are used. Understanding these categories helps in choosing the correct word and phrasing.
Categories of “Withdraw” (Verb)
- Financial: Related to money and banking.
- Military: Related to armed forces and strategic retreat.
- Personal/Social: Related to individual actions and social interactions.
- Legal/Political: Related to laws, statements, and policies.
Categories of “Withdrawal” (Noun)
- Financial: The act of taking money out of an account.
- Medical/Psychological: The state of experiencing symptoms after stopping substance use or social disengagement.
- Military: The act of retreating troops.
- Political/Diplomatic: The act of retracting support or membership.
Examples of Withdraw and Withdrawal
To solidify your understanding, let’s explore numerous examples of “withdraw” and “withdrawal” used in various contexts. These examples are organized into tables for clarity.
Table 1: Examples of “Withdraw” (Verb)
This table provides examples of the verb “withdraw” used in different contexts, showcasing its versatility and range of applications.
| Context | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Financial | I need to withdraw some cash from the ATM. |
| Financial | She decided to withdraw her investment from the risky stock. |
| Financial | He had to withdraw money to pay for his medical expenses. |
| Financial | Can I withdraw funds from this account online? |
| Financial | They had to withdraw a large sum to cover the emergency. |
| Military | The general ordered the troops to withdraw from the battlefield. |
| Military | The army will withdraw its forces as part of the peace treaty. |
| Military | The soldiers were instructed to withdraw under the cover of darkness. |
| Military | We must withdraw our support, as we cannot win this war. |
| Military | The strategy was to withdraw gradually to minimize losses. |
| Personal/Social | After the argument, he tended to withdraw into himself. |
| Personal/Social | She decided to withdraw from the competition due to illness. |
| Personal/Social | He chose to withdraw from the party because he felt unwell. |
| Personal/Social | They asked him to withdraw his nomination for the award. |
| Personal/Social | She decided to withdraw from the group project. |
| Legal/Political | The senator had to withdraw his controversial statement. |
| Legal/Political | The government decided to withdraw the proposed bill. |
| Legal/Political | He was forced to withdraw his lawsuit due to lack of evidence. |
| Legal/Political | The company had to withdraw its product from the market. |
| Legal/Political | They decided to withdraw their support for the candidate. |
| General | The flower will withdraw its petals at night. |
| General | Please withdraw your hand from the machine. |
| General | The cat tried to withdraw its claws. |
| General | Can you withdraw the question you just asked? |
| General | It’s best to withdraw when you know you’re wrong. |
Table 2: Examples of “Withdrawal” (Noun)
This table demonstrates the use of “withdrawal” as a noun, highlighting its role in naming actions, processes, or states.
| Context | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Financial | The bank charges a fee for each withdrawal. |
| Financial | She made a large withdrawal to buy a car. |
| Financial | The withdrawal of funds caused the account to be overdrawn. |
| Financial | He reported an unauthorized withdrawal from his account. |
| Financial | The maximum daily withdrawal is $500. |
| Medical/Psychological | He experienced severe withdrawal symptoms after stopping the medication. |
| Medical/Psychological | She showed signs of social withdrawal following the trauma. |
| Medical/Psychological | The doctor monitored the patient for signs of drug withdrawal. |
| Medical/Psychological | The patient is going through nicotine withdrawal. |
| Medical/Psychological | He suffered from caffeine withdrawal after quitting coffee. |
| Military | The withdrawal of troops was a strategic decision. |
| Military | The army planned a phased withdrawal from the occupied territory. |
| Military | The successful withdrawal saved many lives. |
| Military | The withdrawal was covered by air support. |
| Military | The timing of the withdrawal was crucial. |
| Political/Diplomatic | The country’s withdrawal from the treaty surprised many. |
| Political/Diplomatic | The withdrawal of support led to the project’s cancellation. |
| Political/Diplomatic | Their withdrawal from the alliance weakened the coalition. |
| Political/Diplomatic | The withdrawal of the ambassador signaled a diplomatic crisis. |
| Political/Diplomatic | The public protested the withdrawal of funding for the arts. |
| General | The withdrawal of the offer came as a shock. |
| General | Her sudden withdrawal from the conversation was noticeable. |
| General | The withdrawal of his statement caused confusion. |
| General | The company announced the withdrawal of its new product. |
| General | The team celebrated the successful withdrawal of the climber. |
Table 3: Comparative Examples: Withdraw vs. Withdrawal
This table provides direct comparisons between “withdraw” and “withdrawal” in similar contexts to illustrate their different functions.
| Context | “Withdraw” (Verb) Example | “Withdrawal” (Noun) Example |
|---|---|---|
| Financial | I need to withdraw $200 from my account. | The withdrawal of $200 was processed successfully. |
| Financial | She decided to withdraw all her savings. | The large withdrawal raised some concerns at the bank. |
| Military | The commander ordered the troops to withdraw immediately. | The sudden withdrawal of troops surprised the enemy. |
| Military | They had to withdraw their forces due to heavy losses. | The military’s withdrawal was a strategic move. |
| Personal/Social | He tends to withdraw from social situations when he’s stressed. | His withdrawal from the party was quite noticeable. |
| Personal/Social | She decided to withdraw from the competition due to injury. | Her withdrawal from the race was a disappointment. |
| Legal/Political | The politician had to withdraw his controversial statement. | The withdrawal of his statement caused a media frenzy. |
| Legal/Political | The company decided to withdraw its product from the market. | The product withdrawal was due to safety concerns. |
| Medical | He needed to withdraw from the medication slowly. | He experienced severe withdrawal symptoms. |
| Medical | The doctor advised him to withdraw gradually. | The process of withdrawal can be difficult. |
Usage Rules
The correct usage of “withdraw” and “withdrawal” hinges on understanding their grammatical roles. “Withdraw” is an action, while “withdrawal” is the name of that action or state.
Rule 1: Use “Withdraw” as a Verb
Use “withdraw” to describe the act of removing, retreating, or ceasing involvement. It requires a subject performing the action.
Correct: I withdraw my statement.
Correct: They withdrew their offer.
Incorrect: The withdrawal my statement.
Rule 2: Use “Withdrawal” as a Noun
Use “withdrawal” to refer to the act, process, or state of withdrawing. It can function as a subject, object, or complement in a sentence.
Correct: The withdrawal of funds was authorized.
Correct: He experienced severe withdrawal symptoms.
Incorrect: The withdraw of funds was authorized.
Rule 3: Verb Tense Consistency
Ensure that the verb “withdraw” is conjugated correctly according to the tense of the sentence. Use “withdrew” for past tense and “withdrawn” for past participle.
Correct: She withdrew her application yesterday.
Correct: He has withdrawn all his savings.
Incorrect: She withdraw her application yesterday.
Incorrect: He has withdrew all his savings.
Rule 4: Singular vs. Plural Noun
Remember that “withdrawal” is a singular noun, and its plural form is “withdrawals.”
Correct: One withdrawal was made.
Correct: Multiple withdrawals were made.
Incorrect: One withdrawals was made.
Incorrect: Multiple withdrawal were made.
Common Mistakes
One of the most common mistakes is using “withdraw” as a noun or “withdrawal” as a verb. Recognizing these errors is crucial for improving your grammar.
Mistake 1: Using “Withdraw” as a Noun
Incorrect: The withdraw of the troops was unexpected.
Correct: The withdrawal of the troops was unexpected.
Explanation: “Withdraw” is a verb and cannot be used as the subject of the sentence. “Withdrawal,” the noun form, should be used instead.
Mistake 2: Using “Withdrawal” as a Verb
Incorrect: He will withdrawal his application.
Correct: He will withdraw his application.
Explanation: “Withdrawal” is a noun and cannot function as the main verb in the sentence. “Withdraw,” the verb form, should be used.
Mistake 3: Incorrect Verb Tense
Incorrect: She has withdrew her money from the bank.
Correct: She has withdrawn her money from the bank.
Explanation: When using the present perfect tense, the past participle “withdrawn” should be used, not the past simple “withdrew.”
Mistake 4: Pluralization Errors
Incorrect: There were many withdrawal from the account.
Correct: There were many withdrawals from the account.
Explanation: When referring to multiple instances of withdrawal, the plural form “withdrawals” should be used.
Withdrawaling vs Withdrawing
The correct form is always **withdrawing**. The version **withdrawaling** is incorrect. For example, “They are withdrawing funds from their account” is correct, while “They are withdrawaling funds” is not. Remember, the verb follows standard English participle rules, so there is no “-al” ending.
Withdrawal or Withdrawl / Withdrawl or Withdrawal
A very common spelling error is using **withdrawl** instead of **withdrawal**. The correct noun form always contains an “a” before the final “l.” For instance:
– Correct: “The bank recorded multiple **withdrawals** today.”
– Incorrect: “The bank recorded multiple **withdrawls** today.”
Practice Exercises
Test your understanding of “withdraw” and “withdrawal” with these practice exercises. Choose the correct word to complete each sentence.
Exercise 1: Fill in the Blanks
Choose the correct word (“withdraw” or “withdrawal”) to complete each sentence.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. I need to __________ some money from the ATM. | withdraw |
| 2. The __________ of troops was a strategic decision. | withdrawal |
| 3. She decided to __________ her application to the university. | withdraw |
| 4. He is experiencing __________ symptoms after stopping the medication. | withdrawal |
| 5. The bank charges a fee for each __________. | withdrawal |
| 6. They had to __________ their support for the project. | withdraw |
| 7. The __________ of his statement caused a stir. | withdrawal |
| 8. Can I __________ money from this account online? | withdraw |
| 9. The company announced the __________ of its new product. | withdrawal |
| 10. He will __________ from the competition due to an injury. | withdraw |
Exercise 2: Correct the Sentences
Identify and correct the errors in the following sentences.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. The withdraw of funds was unexpected. | The withdrawal of funds was unexpected. |
| 2. He will withdrawal his application. | He will withdraw his application. |
| 3. She has withdrew her money from the bank. | She has withdrawn her money from the bank. |
| 4. There were many withdrawal from the account. | There were many withdrawals from the account. |
| 5. I want to withdrawal some cash. | I want to withdraw some cash. |
| 6. His withdraw from the group was sudden. | His withdrawal from the group was sudden. |
| 7. They decided to withdrawal their offer. | They decided to withdraw their offer. |
| 8. The military planned a phased withdraw. | The military planned a phased withdrawal. |
| 9. He suffered from caffeine withdraw. | He suffered from caffeine withdrawal. |
| 10. She will withdrawl from society. | She will withdraw from society. |
Exercise 3: Sentence Completion
Complete the following sentences using the correct form of “withdraw” or “withdrawal.”
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. After careful consideration, she decided to __________ her name from the list of candidates. | withdraw |
| 2. The unexpected __________ of the company’s CEO shocked the investors. | withdrawal |
| 3. He had to __________ a large sum of money to cover his daughter’s tuition fees. | withdraw |
| 4. The patient experienced severe __________ symptoms after abruptly stopping the medication. | withdrawal |
| 5. The government’s __________ from the international agreement sparked controversy. | withdrawal |
| 6. They asked him to __________ his comments after they were deemed offensive. | withdraw |
| 7. Making a large __________ can sometimes trigger a flag at the bank. | withdrawal |
| 8. The general ordered his troops to strategically __________ to regroup. | withdraw |
| 9. His sudden __________ from the conversation indicated he was uncomfortable. | withdrawal |
| 10. It’s often better to __________ than to persist in a losing battle. | withdraw |
Advanced Topics
For advanced learners, understanding the nuances and subtle uses of “withdraw” and “withdrawal” is essential. This section delves into more complex aspects.
Figurative Language
Both “withdraw” and “withdrawal” can be used figuratively to describe abstract concepts or emotional states. For example, someone might “withdraw” emotionally from a relationship, or experience “withdrawal” from a previously enjoyed activity.
Example: After the loss, she began to withdraw emotionally from her friends and family.
Example: He experienced a sense of withdrawal from his passion for painting after the accident.
Compound Nouns and Adjectives
While less common, “withdrawal” can sometimes be used in compound nouns or as part of an adjective phrase. These usages often relate to specific contexts, such as finance or medicine.
Example: The bank implemented a new withdrawal policy.
Example: The patient was placed in a withdrawal management program.
Withdrawal as a Process
It’s important to recognize that “withdrawal,” particularly in medical contexts, can refer to a complex and prolonged process, not just a single event. This process involves managing symptoms and supporting the individual through recovery.
Example: The withdrawal process from opioids can be challenging and requires medical supervision.
FAQ
Here are some frequently asked questions about “withdraw” and “withdrawal” to clarify any remaining doubts.
- What is the main difference between “withdraw” and “withdrawal”?The main difference is that “withdraw” is a verb, describing an action, while “withdrawal” is a noun, naming the action or state.
- Can “withdraw” be used as a noun?No, “withdraw” is strictly a verb and cannot be used as a noun. The correct noun form is “withdrawal.”
- What are some common contexts where “withdrawal” is used?“Withdrawal” is commonly used in financial contexts (e.g., bank withdrawals), medical contexts (e.g., drug withdrawal), and military contexts (e.g., troop withdrawal).
- How do I use “withdraw” in the past tense?The past tense of “withdraw” is “withdrew.” For the past participle, use “withdrawn.” For example: “He withdrew his application yesterday,” and “He has withdrawn all his savings.”
- Is “withdrawals” the plural form of “withdrawal”?Yes, “withdrawals” is the plural form of “withdrawal.” For example: “There were multiple withdrawals from the account.”
- How do I avoid confusing “withdraw” and “withdrawal” in my writing?Pay attention to the context and the grammatical role the word needs to play in the sentence. If you need a verb describing an action, use “withdraw.” If you need a noun naming an action or state, use “withdrawal.”
- Can “withdrawal” ever be used in a positive context?While often associated with negative situations like medical withdrawal, “withdrawal” can be neutral or even positive in contexts like a strategic military withdrawal to regroup forces.
- What is the difference between “retreat” and “withdraw” in a military context?While similar, “retreat” often implies a disorganized or forced movement, while “withdraw” suggests a more planned and strategic movement. “Withdraw” is generally more formal and controlled.
Conclusion
Mastering the distinction between “withdraw” and “withdrawal” is essential for accurate and effective communication in English. By understanding their definitions, grammatical functions, and usage rules, you can confidently use these words in various contexts.
Remember that “withdraw” is a verb describing the action of removing or retreating, while “withdrawal” is a noun referring to the act or state of withdrawing.
Continue practicing with examples and exercises to reinforce your understanding. Pay close attention to the context and grammatical role of the word in each sentence.
With consistent effort, you’ll be able to avoid common mistakes and use “withdraw” and “withdrawal” correctly in your writing and speech. Remember, language learning is a journey, and every step you take brings you closer to fluency and mastery.